How to use Content Groups for better SEO Analytics
Content groups can be helpful to analyze search traffic for multiple pages at once. This guide will show you how to set them up and use them.
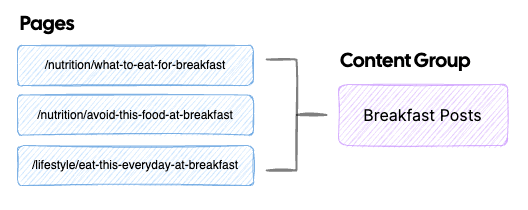
What are Content Groups?
Content groups help you analyze search performance of multiple pages that have something in common. As an example, you could group all your blog posts to see how your blog is performing. Or you could group only pages related to breakfast. Instead of analyzing performance for a single page, you can see how the whole group is doing. Even if one page is getting less traffic, the overall group might be still be doing well.
Here’s a few different ways you can use content groups:
- All blog posts: useful to see how your blog is doing overall compared to other pages;
- Group product pages by category to see how each category is doing;
- Group pages that reference a specific keyword that’s important to your niche;
- Group all your SaaS landing pages if you have multiple;
- Group your pSEO pages if you’re doing programmatic SEO.
If you’re using Google Search Console, you’d need to use Regular Expressions to simulate content groups. However, you can’t save them, so you need to type them every time you want to see the data. In SEO Gets, you can save your content groups and easily monitor them over time.
How to set up Content Groups in SEO Gets
In SEO Gets, you can set up content groups by using a simple pattern matching system, as well as advanced regex matching. Here’s an example of how you might set up a group of all blog posts.
First select the site you want to create a group, and click on the Settings tab at the top.
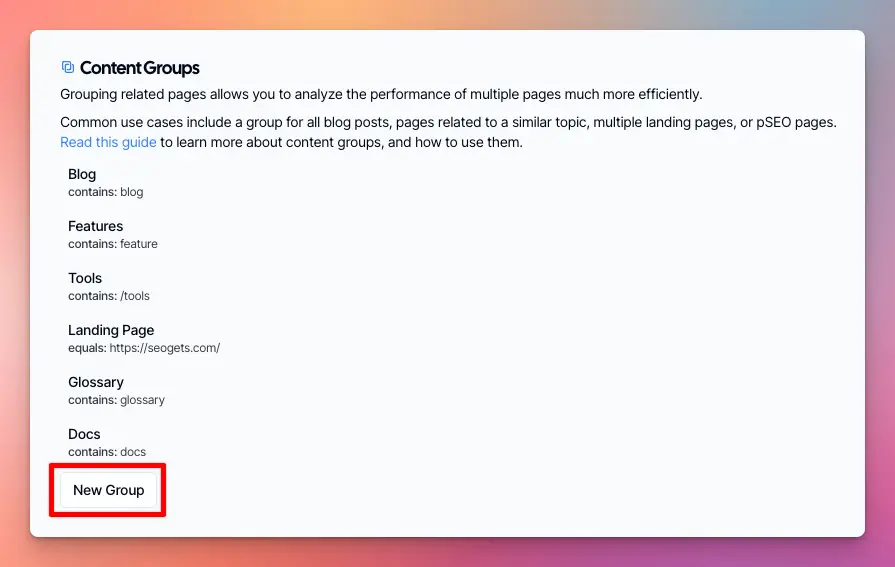
Then find the Content Groups section, click on New Group.
Enter a name to label the Content Group, and define one or more conditions. Use the and.. button to add additional conditions. You can add as many groups as you want, and change them at any time.
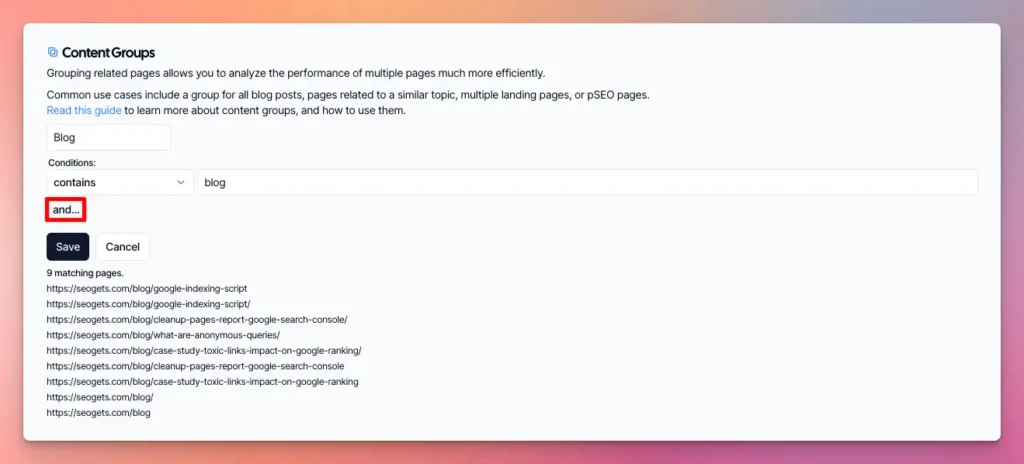
Here’s a few examples of popular conditions you can use to match pages.
- Contains: Pulls URLs that contain the keyword you specify.
- Doesn’t Contain: Pulls URLs that do not contain the keyword you specify. This is essentially the opposite of the “Contains” condition.
- Matches Any (Batch): Pulls URLs that match any of the keywords or patterns you specify in a batch. This allows you to create a list of multiple terms or regular expressions, and the condition will be met if the URL matches any one of them.
- Doesn’t Match Any (Batch): Pulls URLs that do not match any of the keywords or patterns you specify in a batch. This is the opposite of “Matches Any (Batch)”. It allows you to create a list of multiple terms or regular expressions, and the condition will be met only if the URL doesn’t match any of them.
Content Groups for Programmatic SEO (pSEO)
Content Groups can be very useful for sites doing programmatic SEO (pSEO). pSEO pages are pages that are generated by a program, such as a blog post, or a product page and they usually have a common structure.
stagetimer.io is a great example of a website using pSEO. They have hundreds of pages like this https://stagetimer.io/go/1-minute/ and they all start with /go. Instead of analyzing each page individually, they can use content groups to analyze all of their pSEO pages at once.
How to use Content Groups for analytics
After setting up your content groups, you’ll find them in your site analytics under the Content Groups section. I’ll look like this:
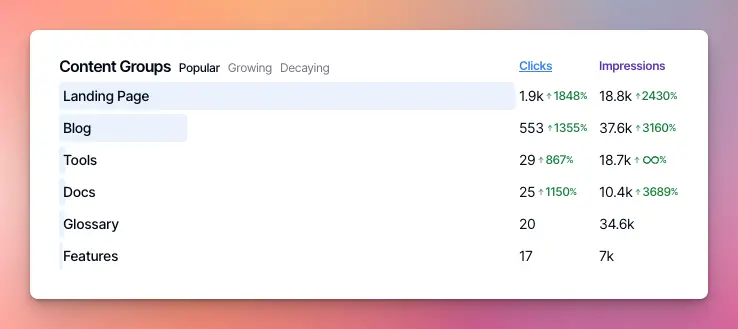
You can also drill down into each content group to see how individual pages are performing, what keywords they’re ranking for, and more. Click on the content group you want to analyze and the dashboard will be filtered to only include data related to pages in that group.
Here’s an example of what that might look like:
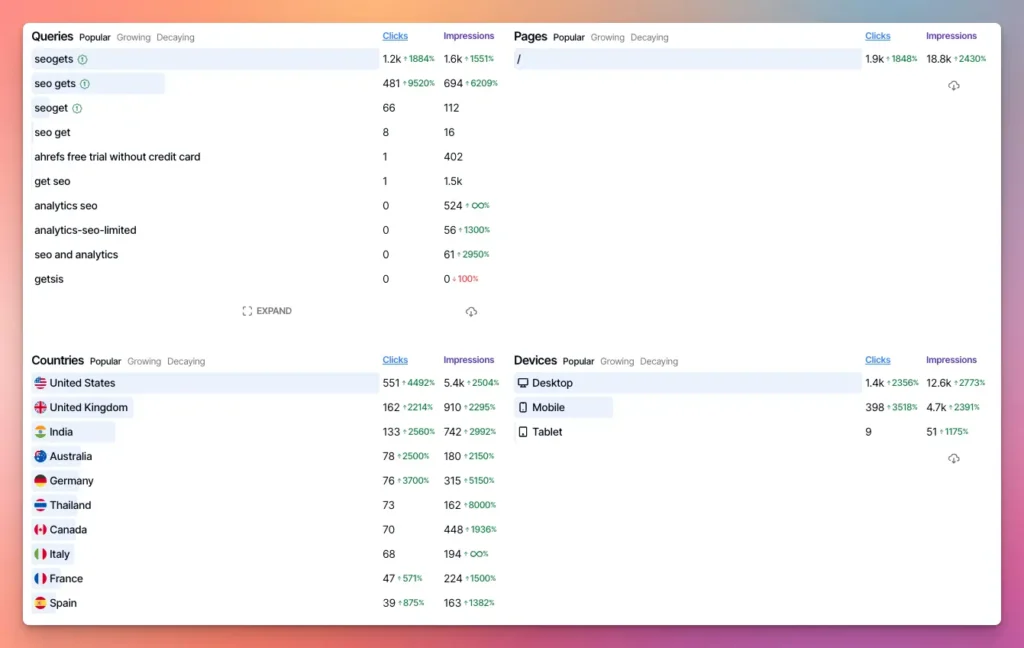
The image above shows me the top 10 pages in this content group, as well as the top 10 queries they’re ranking for, and much more. As usual, you can click on any of the pages or queries to see more details, or see what pages are growing/decaying the most.
✨ Interested in simplifying your SEO analytics workflow? Try SEO Gets for free.